How To Find The Domain And Range Of Points
We are familiar with the terms Domain of a Function and Range of a Function. But what does information technology mean? Before diving deeper into the topic, let us understand what a office is?
Functions:
Functions are ane of the fundamental concepts in mathematics which take got numerous applications in the real world. Exist it the mega skyscrapers or super-fast cars, and their modelling requires methodical application of functions. Almost all real-globe problems are formulated, interpreted, and solved using functions.
An understanding of relations is required in order to understand functions. Knowledge of Cartesian products is required to empathize relations. A Cartesian product of two sets
\(\begin{array}{50}A\terminate{array} \)
and\(\begin{array}{l}B\end{array} \)
is collection of all the ordered pairs\(\begin{assortment}{l}(a,b)\stop{array} \)
such that\(\brainstorm{array}{l}a ∈ A\end{assortment} \)
and\(\begin{assortment}{l}b ∈ B\terminate{array} \)
. A relation is a subset of a Cartesian product. Hence, a relation is a rule that "relates" an element from 1 prepare to an element from some other prepare. A function is a special kind of relation. Let us consider a relation\(\begin{array}{50}F\finish{assortment} \)
from set\(\brainstorm{array}{50}A\finish{assortment} \)
to\(\begin{array}{l}B\end{array} \)
.Definition 1: A relation
\(\begin{assortment}{l}F\stop{array} \)
is said to be a function if each element in prepare\(\begin{array}{l}A\end{array} \)
is associated with exactly one element in set\(\begin{array}{l}B\end{assortment} \)
.To empathise the divergence betwixt relations and functions, permit us have an example. Set
\(\begin{array}{l}A\end{array} \)
contains the name of all the countries that accept won the cricket world loving cup and set\(\begin{array}{fifty}B\end{array} \)
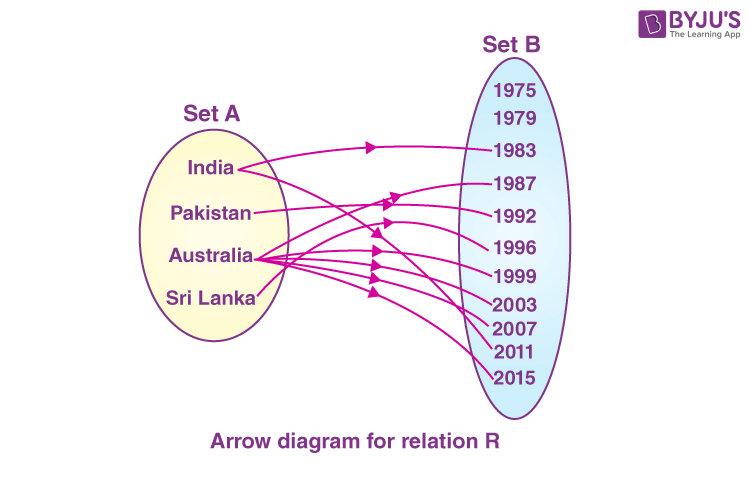
contains the listing of years in which the world cup was played. The arrow diagram in fig.1 represents a relation\(\begin{array}{l}R\end{array} \)
but non a function. This is because elements in the set\(\begin{array}{l}A\end{array} \)
are associated with more than one chemical element in the set\(\begin{array}{l}B\end{array} \)
. 
But if we define a relation
\(\brainstorm{array}{l}F\terminate{array} \)
from the set\(\begin{array}{l}A\end{array} \)
to\(\begin{assortment}{50}B\finish{assortment} \)
such that information technology assembly the countries with the year in which, they won the world cup for the first fourth dimension. Thus, for every chemical element in the prepare\(\begin{array}{l}A\end{assortment} \)
, nosotros accept exactly 1 clan in the set\(\begin{array}{l}B\end{array} \)
. This relation\(\brainstorm{array}{50}F\stop{array} \)
shown in fig. 2 qualifies to be a role. 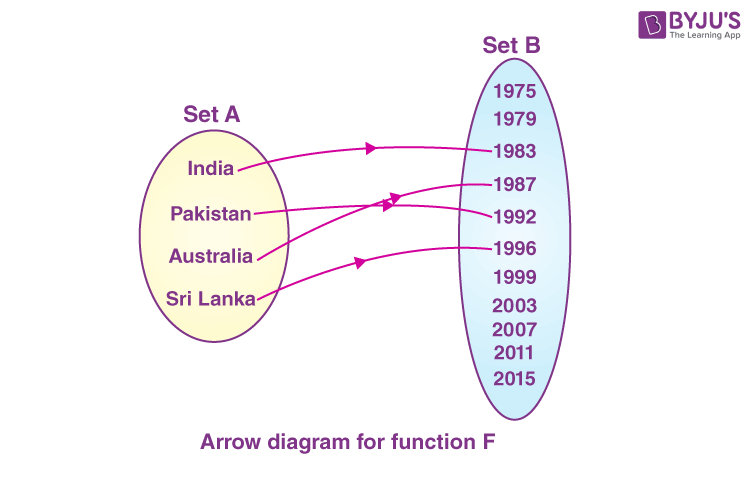
Remember that in the case of a relation, the domain might not be the aforementioned as the left set in the pointer diagram. This is because the set may incorporate any element which doesn't take an image in the right set. But in the case of functions, the domain volition always be equal to the starting time prepare. Range and Codomain of a part are divers in the same style as they are divers for relations.
Domain and Range
The domain and range of a function can exist identified based on the possibility of the given function to be defined in the existent set. Let's take a look at Domain and Range that is given in detail here.
Domain
The prepare of all possible values which qualify as inputs to a office is known as the domain of the office, or it tin as well be divers as the entire set of values possible for independent variables. The domain tin can be found in – the denominator of the fraction is not equal to zero and the digit under the foursquare root bracket is positive. (In the example of a function with fraction values).
For due east.1000. the domain of the part F is set A i.e. {Bharat, Islamic republic of pakistan, Australia, Sri Lanka}.
How to Find the Domain of a office
- To discover the domain, nosotros need to expect at the values of the independent variables which are allowed to use as explained to a higher place, i.due east. no zero at the bottom of fraction and no negative sign inside the square root.
- In full general, the set of all real numbers (R) is considered as the domain of a function subject to some restrictions. They are:
When the given part is of the grade f(x) = 2x + 5 or f(x) = x2 – 2, the domain will exist "the set of all real numbers.
When the given office is of the course f(x) = i/(ten – 1), the domain will be the set of all existent numbers except 1. - In some cases, the interval exist specified along with the function such every bit f(10) = 3x + iv, 2 < x < 12. Hither, x tin can accept the values between 2 and 12 equally input (i.e. domain).
- Domain restrictions refer to the values for which the given function cannot be defined.
Also, try: Domain and Range Calculator
Range
The set of all the outputs of a part is known as the range of the function or subsequently substituting the domain, the entire set of all values possible every bit outcomes of the dependent variable.
For e.yard. the range of the function F is {1983, 1987, 1992, 1996}. On the other hand, the whole set B is known equally the codomain of the function. It is the set that contains all the outputs of the function. So, the set of real numbers is a codomain for every real-valued function. The codomain of the functionF is prepare B.
Video Lesson
Range of a Function
How to Observe the Range of a Part
Consider a role y = f(x).
- The spread of all the y values from minimum to maximum is the range of the function.
- In the given expression of y, substitute all the values of x to cheque whether it is positive, negative or equal to other values.
- Detect the minimum and maximum values for y.
- And then draw a graph for the same.
An interesting signal almost the range and codomain is that "it is possible to restrict the range (i.east. the output of a part) by redefining the codomain of that office". For case, the codomain of f(x) must be the set of all positive integers or negative existent numbers and so on. Here, the output of the function must be a positive integer and the domain will too be restricted accordingly in this case.
Till now, we accept represented functions with upper example messages simply they are generally represented by lower case letters. If f is a office from set A to B and (a,b) ∈ f, then f(a) = b. b is called the image of a nether f and a is called the preimage of b under f .
Summary:
- The domain is defined as the entire ready of values possible for independent variables.
- The Range is constitute after substituting the possible x- values to find the y-values.
Solved Examples
Case i:
Find the domain and range of a function f(10) = 3x2 – five.
Solution:
Given part:
f(x) = 3xtwo – 5
We know that the domain of a function is the set of input values for f, in which the office is existent and defined.
The given role has no undefined values of x.
Thus, for the given function, the domain is the set of all existent numbers.
Domain = [- ∞, ∞]
Also, the range of a role comprises the set of values of a dependent variable for which the given function is defined.
Ley y = 3xtwo – 5
3x2 = y + v
ten2 = (y + 5)/3
10 = √[(y + 5)/three]
Square root part will be defined for non-negative values.
Then, √[(y + 5)/iii] ≥ 0
This is possible when y is greater than y ≥ -5.
Hence, the range of f(x) is [-five, ∞).
Instance 2:
Find the domain and range of a function f(x) = (2x – 1)/(x + iv).
Solution:
Given function is:
f(x) = (2x – 1)/(x + iv)
We know that the domain of a function is the set of input values for f, in which the function is real and divers.
The given function is not defined when x + 4 = 0, i.due east. x = -4
So, the domain of given part is the set of all real number except -4.
i.e. Domain = (-∞, -4) U (-4, ∞)
Also, the range of a office comprises the prepare of values of a dependent variable for which the given function is defined.
Let y = (2x – 1)/(x + 4)
xy + 4y = 2x – ane
2x – xy = 4y + ane
ten(2 – y) = 4y + ane
ten = (4y + 1)/(2 – y)
This is defined only when y is non equal to 2.
Hence, the range of the given function is (-∞, 2) U (ii, ∞).
Video Lesson
Domain, Range and Period of Role
At that place are several types of functions and some of them have got funny names eastward.g. flooring function, ceiling function, etc. To know more, visit www.byjus.com and experience fun in learning.
How To Find The Domain And Range Of Points,
Source: https://byjus.com/maths/domain-codomain-range-functions/
Posted by: ferrantelittly.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find The Domain And Range Of Points"
Post a Comment